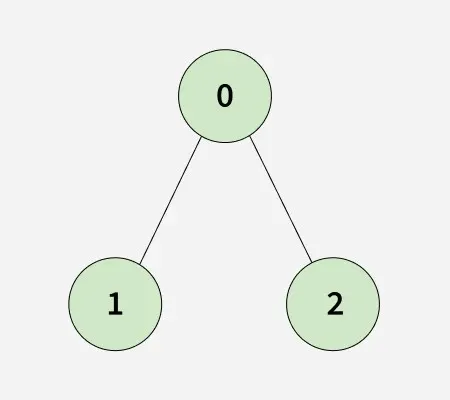
Verilen bir bağlı yönlendirilmemiş grafik bitişiklik listesiyle temsil edilir adjList[][] ile N düğümler ve M her düğümün sahip olduğu kenarlar farklı etiket itibaren 0'dan n-1'e ve her adj[i], i köşe noktasına bağlı köşelerin listesini temsil eder.
Bir oluştur klon grafikteki her düğümün bir tamsayı içerdiği grafiğin val ve bir dizi ( komşular ) düğümlerin geçerli düğüme bitişik düğümleri içerir.
sınıf Düğümü {
val: tamsayı
komşular: Liste[Düğüm]
}
Göreviniz verilen grafiği klonlamak ve klonlanan grafiğe bir referans döndürmektir.
Not: Verilen grafiğin doğru bir kopyasını döndürürseniz çıktı doğru olacaktır; aksi takdirde kopya hatalıysa yanlış yazdırılacaktır.
Örnekler
Giriş: n = 4 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0 2] [0 1 3] [2]]
Çıkış: doğru
Açıklama:
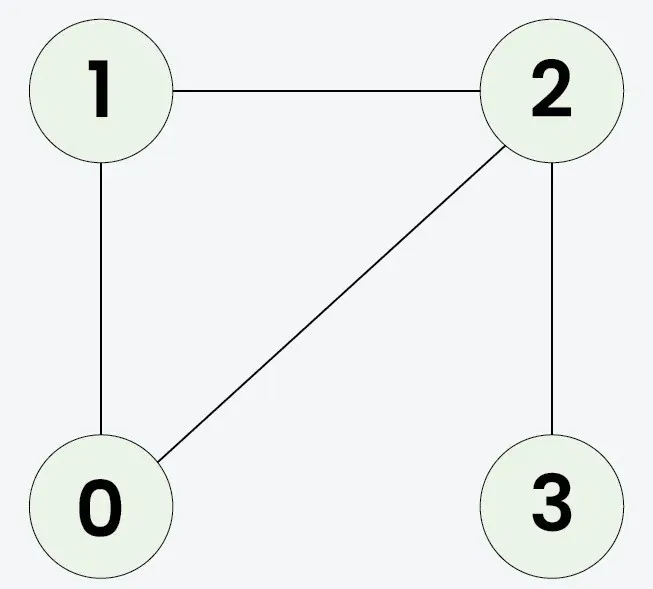
Klonlanan grafik orijinaliyle aynı olduğundan çıktı doğru olacaktır.Giriş: n = 3 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0] [0]]
Çıkış: doğru
Açıklama:
Klonlanan grafik orijinaliyle aynı olduğundan çıktı doğru olacaktır.
İçerik Tablosu
- Ziyaret edilen/klonlanan düğümleri neden takip etmemiz gerekiyor?
- Ziyaret edilen/klonlanan düğümlerin takibi nasıl yapılır?
- Klon düğümleri nasıl bağlanır?
- Klonlanmış grafiğin doğru olup olmadığı nasıl doğrulanır?
- [Yaklaşım 1] BFS geçişini kullanma - O(V+E) Zaman ve O(V) Uzay
- [Yaklaşım 2] DFS geçişini kullanma - O(V+E) Zaman ve O(V) Uzay
Ziyaret edilen/klonlanan düğümleri neden takip etmemiz gerekiyor?
Bir grafiği klonlarken sonsuz özyinelemeyi ve gereksiz çalışmayı önlemek için ziyaret edilen veya klonlanan düğümleri izlememiz gerekir. Grafikler döngüler içerebildiğinden (burada bir düğüm daha önce ziyaret edilen bir düğüme işaret edebilir), zaten klonladığımız düğümleri takip etmeden, klonlama işlevi aynı düğümleri sonsuza kadar tekrar ziyaret ederek yığın taşmasına veya hatalı çoğaltmaya neden olur.
Ziyaret edilen/klonlanan düğümlerin takibi nasıl yapılır?
Halihazırda oluşturulmuş tüm düğümleri korumak için bir HashMap/Map gereklidir. Anahtar mağazalar : Orijinal Düğümün Referansı/Adresi Değer depoları : Klonlanan Düğümün Referansı/Adresi Tüm grafik düğümlerinin bir kopyası oluşturuldu.
Klon düğümleri nasıl bağlanır?
Bir bölgenin komşu köşelerini ziyaret ederken düğüm içinde karşılık gelen klonu alın düğüm senin için buna diyelim İÇİNDE şimdi tüm komşu düğümleri ziyaret edin içinde ve her komşu için karşılık gelen klon düğümünü bulun (bulunmazsa bir tane oluşturun) ve ardından komşu vektöre itin İÇİNDE düğüm.
Klonlanmış grafiğin doğru olup olmadığı nasıl doğrulanır?
Klonlamadan önce orijinal grafik üzerinde ve klonlama tamamlandıktan sonra tekrar klonlanmış grafik üzerinde bir BFS geçişi gerçekleştirin. Her geçiş sırasında her düğümün değeri, adresi (veya referansı) ile birlikte yazdırılır. Klonlamanın doğruluğunu doğrulamak için her iki geçişte ziyaret edilen düğümlerin sırasını karşılaştırın. Düğüm değerleri aynı sırada görünüyor ancak adresleri (veya referansları) farklıysa, grafiğin başarıyla ve doğru şekilde kopyalandığı doğrulanır.
Nasıl yapılacağını keşfedin birden fazla bağlı bileşene sahip grafikler içeren yönlendirilmemiş bir grafiği klonlayın Tüm düğümlerin ve kenarların tam bir derin kopyasını sağlamak için BFS veya DFS'yi kullanın.
Java'ya göre liste sıralama
[Yaklaşım 1] BFS geçişini kullanma - O(V+E) Zaman ve O(V) Uzay
C++BFS yaklaşımında grafik bir kuyruk kullanılarak yinelemeli olarak klonlanır. İlk düğümü klonlayıp kuyruğa yerleştirerek başlıyoruz. Sıradaki her düğümü işlerken komşularını ziyaret ederiz. Eğer bir komşu henüz klonlanmamışsa, onu bir haritada saklayan bir klon oluştururuz ve daha sonra işlenmek üzere sıraya koyarız. Daha sonra komşunun klonunu mevcut düğümün klonunun komşular listesine ekliyoruz. Bu süreç, tüm düğümlerin genişlik öncelikli olarak ziyaret edilmesini sağlayarak seviye seviye devam eder. BFS, özellikle derin yinelemelerden kaçınmak ve büyük veya geniş grafikleri verimli bir şekilde işlemek için kullanışlıdır.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { public int val; public ArrayList<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Map<Node Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Clone the starting node Node clone = new Node(node.val); mp.put(node clone); q.offer(node); while (!q.isEmpty()) { Node current = q.poll(); for (Node neighbor : current.neighbors) { // Clone neighbor if it hasn't been cloned yet if (!mp.containsKey(neighbor)) { mp.put(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.offer(neighbor); } // Add the clone of the neighbor to the current node's clone mp.get(current).neighbors.add(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node2 node3))); node2.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node3))); node3.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node2 node4))); node4.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node3))); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static boolean compareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || n1 == n2) return false; visited.put(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.size() != n2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node neighbor1 = n1.neighbors.get(i); Node neighbor2 = n2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) != neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); boolean isEqual = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
from collections import deque # Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0): self.val = val self.neighbors = [] # Clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): if not node: return None # Map to hold original nodes as keys and their clones as values mp = {} # Initialize BFS queue q = deque([node]) # Clone the starting node mp[node] = Node(node.val) while q: current = q.popleft() for neighbor in current.neighbors: # If neighbor not cloned yet if neighbor not in mp: mp[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val) q.append(neighbor) # Link clone of neighbor to the clone of the current node mp[current].neighbors.append(mp[neighbor]) return mp[node] # Build graph def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs structurally and by values def compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): if not n1 or not n2: return n1 == n2 if n1.val != n2.val or n1 is n2: return False visited[n1] = n2 if len(n1.neighbors) != len(n2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(n1.neighbors)): neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i] neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i] if neighbor1 in visited: if visited[neighbor1] != neighbor2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited): return False return True # Driver if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() cloned = cloneGraph(original) result = compareGraphs(original cloned {}) print('true' if result else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Definition for a Node public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; var mp = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); var q = new Queue<Node>(); // Clone the starting node var clone = new Node(node.val); mp[node] = clone; q.Enqueue(node); while (q.Count > 0) { var current = q.Dequeue(); foreach (var neighbor in current.neighbors) { // If neighbor not cloned clone it and enqueue if (!mp.ContainsKey(neighbor)) { mp[neighbor] = new Node(neighbor.val); q.Enqueue(neighbor); } // Add clone of neighbor to clone of current mp[current].neighbors.Add(mp[neighbor]); } } return mp[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { var node1 = new Node(0); var node2 = new Node(1); var node3 = new Node(2); var node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node2 node3 }); node2.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node3 }); node3.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node2 node4 }); node4.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node3 }); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static bool CompareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || ReferenceEquals(n1 n2)) return false; visited[n1] = n2; if (n1.neighbors.Count != n2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.Count; i++) { var neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; var neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(neighbor1)) { if (!ReferenceEquals(visited[neighbor1] neighbor2)) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void Main() { var original = BuildGraph(); var cloned = CloneGraph(original); var visited = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); Console.WriteLine(CompareGraphs(original cloned visited) ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Clone the graph function cloneGraph(node) { if (!node) return null; const mp = new Map(); const q = [node]; // Clone the initial node mp.set(node new Node(node.val)); while (q.length > 0) { const current = q.shift(); for (const neighbor of current.neighbors) { if (!mp.has(neighbor)) { mp.set(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.push(neighbor); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current mp.get(current).neighbors.push(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors = [node2 node3]; node2.neighbors = [node1 node3]; node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4]; node4.neighbors = [node3]; return node1; } // Compare two graphs structurally and by value function compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited = new Map()) { if (!n1 || !n2) return n1 === n2; if (n1.val !== n2.val || n1 === n2) return false; visited.set(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.length !== n2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.length; i++) { const neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; const neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) !== neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver const original = buildGraph(); const cloned = cloneGraph(original); const result = compareGraphs(original cloned); console.log(result ? 'true' : 'false');
Çıkış
true
[Yaklaşım 2] DFS geçişini kullanma - O(V+E) Zaman ve O(V) Uzay
C++DFS yaklaşımında grafik özyineleme kullanılarak klonlanır. Verilen düğümden başlıyoruz ve geri izlemeden önce her dal boyunca mümkün olduğunca uzağa keşfediyoruz. Aynı düğümün birden çok kez işlenmesini önlemek ve döngüleri işlemek için önceden klonlanmış düğümlerin izini sürmek için bir harita (veya sözlük) kullanılır. Bir düğümle ilk kez karşılaştığımızda onun bir kopyasını oluşturur ve onu haritaya kaydederiz. Daha sonra o düğümün her bir komşusu için onu yinelemeli olarak klonlarız ve klonlanan komşuyu mevcut düğümün klonuna ekleriz. Bu, tüm düğümlerin geri dönmeden önce derinlemesine ziyaret edilmesini ve grafik yapısının aslına uygun şekilde kopyalanmasını sağlar.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { int val; ArrayList<Node> neighbors; Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Map to hold original node to its copy static HashMap<Node Node> copies = new HashMap<>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.containsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies.put(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node2 node3)); node2.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1 node3)); node3.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1node2 node4)); node4.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node3)); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static boolean compareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited.put(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.size() != node2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors.get(i); Node n2 = node2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) != n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph boolean result = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(result ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
# Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0 neighbors=None): self.val = val self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else [] # Map to hold original node to its copy copies = {} # Function to clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): # If the node is None return None if not node: return None # If node is not yet cloned clone it if node not in copies: # Create a clone of the node clone = Node(node.val) copies[node] = clone # Recursively clone neighbors for neighbor in node.neighbors: clone.neighbors.append(cloneGraph(neighbor)) # Return the clone return copies[node] def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs for structural and value equality def compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited): if not node1 or not node2: return node1 == node2 if node1.val != node2.val or node1 is node2: return False visited[node1] = node2 if len(node1.neighbors) != len(node2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(node1.neighbors)): n1 = node1.neighbors[i] n2 = node2.neighbors[i] if n1 in visited: if visited[n1] != n2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() # Clone the graph using DFS cloned = cloneGraph(original) # Compare original and cloned graph visited = {} print('true' if compareGraphs(original cloned visited) else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Dictionary to hold original node to its copy static Dictionary<Node Node> copies = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.ContainsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies[node] = clone; // Recursively clone neighbors foreach (Node neighbor in node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.Add(CloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.Add(node2); node1.neighbors.Add(node3); node2.neighbors.Add(node1); node2.neighbors.Add(node3); node3.neighbors.Add(node1); node3.neighbors.Add(node2); node3.neighbors.Add(node4); node4.neighbors.Add(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static bool CompareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited[node1] = node2; if (node1.neighbors.Count != node2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.Count; i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; Node n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(n1)) { if (visited[n1] != n2) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { Node original = BuildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS Node cloned = CloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph bool isEqual = CompareGraphs(original cloned new Dictionary<Node Node>()); Console.WriteLine(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Map to hold original node to its copy const copies = new Map(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS function cloneGraph(node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node === null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.has(node)) { const clone = new Node(node.val); copies.set(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (let neighbor of node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.push(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.push(node2 node3); node2.neighbors.push(node1 node3); node3.neighbors.push(node1 node2 node4); node4.neighbors.push(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality function compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited = new Map()) { if (!node1 || !node2) return node1 === node2; if (node1.val !== node2.val || node1 === node2) return false; visited.set(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.length !== node2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.length; i++) { const n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; const n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) !== n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code const original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS const cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph console.log(compareGraphs(original cloned) ? 'true' : 'false');
Çıkış
true