Dizi, bitişik bellek konumlarında depolanan benzer türde veri öğelerinin toplanması olarak tanımlanır. Diziler, C programlama dilinde int, char, double, float vb. gibi ilkel veri türlerini depolayabilen türetilmiş veri türüdür. Ayrıca işaretçiler, yapı gibi türetilmiş veri türlerinin koleksiyonunu saklama özelliğine de sahiptir. vb. Dizi, her veri öğesine indeks numarası kullanılarak rastgele erişilebilen en basit veri yapısıdır.
Benzer öğeleri depolamanız gerekiyorsa C dizisi faydalıdır. Örneğin bir öğrencinin 6 dersteki notlarını saklamak istiyorsak farklı ders notları için farklı değişkenler tanımlamamıza gerek yoktur. Bunun yerine her bir konudaki işaretleri bitişik hafıza konumlarında saklayabilen bir dizi tanımlayabiliriz.
Diziyi kullanarak elemanlara kolaylıkla erişebiliriz. Dizinin elemanlarına erişmek için yalnızca birkaç satır kod gerekir.
Dizinin Özellikleri
Dizi aşağıdaki özellikleri içerir.
- Bir dizinin her öğesi aynı veri türündedir ve aynı boyuttadır, yani int = 4 bayt.
- Dizinin elemanları, ilk elemanın en küçük hafıza konumunda depolandığı bitişik hafıza konumlarında saklanır.
- Dizinin her bir elemanının adresini, verilen temel adres ve veri elemanının boyutu ile hesaplayabildiğimiz için, dizinin elemanlarına rastgele erişilebilir.
C Dizisinin Avantajı
1) Kod Optimizasyonu : Verilere erişim için daha az kod.
2) Geçiş kolaylığı : For döngüsünü kullanarak bir dizinin elemanlarını kolayca alabiliriz.
3) Sıralama kolaylığı : Dizinin elemanlarını sıralamak için yalnızca birkaç satır koda ihtiyacımız var.
4) Rastgele Erişim : Diziyi kullanarak herhangi bir öğeye rastgele erişebiliriz.
C Dizisinin Dezavantajı
1) Sabit Boyut : Dizinin bildirimi sırasında tanımladığımız boyut ne olursa olsun sınırı aşamayız. Yani daha sonra öğreneceğimiz LinkedList gibi dinamik olarak boyut büyümüyor.
C Dizisinin Bildirisi
C dilinde bir diziyi aşağıdaki şekilde deklare edebiliriz.
data_type array_name[array_size];
Şimdi diziyi bildirmek için örneği görelim.
int marks[5];
Burada int veri tipi , işaretler dizi_adı ve 5 dizi_boyutu .
C Dizisinin Başlatılması
Bir diziyi başlatmanın en basit yolu, her elemanın indeksini kullanmaktır. Dizinin her elemanını indeksi kullanarak başlatabiliriz. Aşağıdaki örneği düşünün.
dize yöntemleri
marks[0]=80;//initialization of array marks[1]=60; marks[2]=70; marks[3]=85; marks[4]=75;
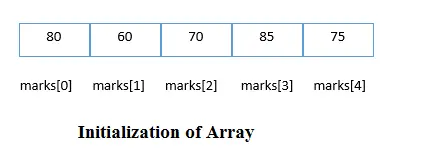
C dizisi örneği
#include int main(){ int i=0; int marks[5];//declaration of array marks[0]=80;//initialization of array marks[1]=60; marks[2]=70; marks[3]=85; marks[4]=75; //traversal of array for(i=0;i<5;i++){ printf('%d
',marks[i]); } end of for loop return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 80 60 70 85 75 </pre> <h2>C Array: Declaration with Initialization</h2> <p>We can initialize the c array at the time of declaration. Let's see the code.</p> <pre> int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60}; </pre> <p>In such case, there is <strong>no requirement to define the size</strong> . So it may also be written as the following code.</p> <pre> int marks[]={20,30,40,50,60}; </pre> <p>Let's see the C program to declare and initialize the array in C.</p> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=0; int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60};//declaration and initialization of array //traversal of array for(i=0;i<5;i++){ printf('%d
',marks[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 30 40 50 60 </pre> <h2>C Array Example: Sorting an array</h2> <p>In the following program, we are using bubble sort method to sort the array in ascending order.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i, j,temp; int a[10] = { 10, 9, 7, 101, 23, 44, 12, 78, 34, 23}; for(i = 0; i<10; i++) { for(j="i+1;" j a[i]) temp="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="temp;" } printf('printing sorted element list ...
'); for(i="0;" i<10; printf('%d
',a[i]); < pre> <h2>Program to print the largest and second largest element of the array.</h2> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[100],i,n,largest,sec_largest; printf('Enter the size of the array?'); scanf('%d',&n); printf('Enter the elements of the array?'); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { scanf('%d',&arr[i]); } largest="arr[0];" sec_largest="arr[1];" for(i="0;ilargest)" else if (arr[i]>sec_largest && arr[i]!=largest) { sec_largest=arr[i]; } } printf('largest = %d, second largest = %d',largest,sec_largest); } </n;></pre> <hr></10;></pre></5;i++){></pre></5;i++){> C Dizisi: Başlatma ile Bildirim
Bildirim sırasında c dizisini başlatabiliriz. Kodu görelim.
int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60}; Böyle bir durumda boyutu tanımlamaya gerek yok . Yani aşağıdaki kod olarak da yazılabilir.
int marks[]={20,30,40,50,60}; C'deki diziyi bildiren ve başlatan C programını görelim.
#include int main(){ int i=0; int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60};//declaration and initialization of array //traversal of array for(i=0;i<5;i++){ printf(\'%d
\',marks[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 30 40 50 60 </pre> <h2>C Array Example: Sorting an array</h2> <p>In the following program, we are using bubble sort method to sort the array in ascending order.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i, j,temp; int a[10] = { 10, 9, 7, 101, 23, 44, 12, 78, 34, 23}; for(i = 0; i<10; i++) { for(j="i+1;" j a[i]) temp="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="temp;" } printf(\'printing sorted element list ...
\'); for(i="0;" i<10; printf(\'%d
\',a[i]); < pre> <h2>Program to print the largest and second largest element of the array.</h2> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[100],i,n,largest,sec_largest; printf('Enter the size of the array?'); scanf('%d',&n); printf('Enter the elements of the array?'); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i]); } largest="arr[0];" sec_largest="arr[1];" for(i="0;ilargest)" else if (arr[i]>sec_largest && arr[i]!=largest) { sec_largest=arr[i]; } } printf('largest = %d, second largest = %d',largest,sec_largest); } </n;></pre> <hr></10;></pre></5;i++){> C Dizisi Örneği: Bir diziyi sıralama
Aşağıdaki programda diziyi artan düzende sıralamak için kabarcık sıralama yöntemini kullanıyoruz.
#include void main () { int i, j,temp; int a[10] = { 10, 9, 7, 101, 23, 44, 12, 78, 34, 23}; for(i = 0; i<10; i++) { for(j="i+1;" j a[i]) temp="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="temp;" } printf(\'printing sorted element list ...
\'); for(i="0;" i<10; printf(\'%d
\',a[i]); < pre> <h2>Program to print the largest and second largest element of the array.</h2> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[100],i,n,largest,sec_largest; printf('Enter the size of the array?'); scanf('%d',&n); printf('Enter the elements of the array?'); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i]); } largest="arr[0];" sec_largest="arr[1];" for(i="0;ilargest)" else if (arr[i]>sec_largest && arr[i]!=largest) { sec_largest=arr[i]; } } printf('largest = %d, second largest = %d',largest,sec_largest); } </n;></pre> <hr></10;> 