 #practiceLinkDiv { görüntü: yok !önemli; }
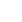
#practiceLinkDiv { görüntü: yok !önemli; }Her düzeyin en uç köşelerinin ikili ağaç baskı düğümleri verilmiştir ancak alternatif sıradadır.
Örnek:

For above tree the output can be 1 2 7 8 31 - print rightmost node of 1st level - print leftmost node of 2nd level - print rightmost node of 3rd level - print leftmost node of 4th level - print rightmost node of 5th level OR 1 3 4 15 16 - print leftmost node of 1st level - print rightmost node of 2nd level - print leftmost node of 3rd level - print rightmost node of 4th level - print leftmost node of 5th levelRecommended Practice Alternatif sırayla aşırı düğümler Deneyin!
Buradaki fikir, ağacı seviye seviye geçmektir. Her seviye için, içindeki düğümlerin sayısını sayarız ve Boole bayrağının değerine göre en soldaki veya en sağdaki düğümü yazdırırız. Mevcut seviyedeki tüm düğümleri kuyruğa alırız ve sonraki seviyedeki tüm düğümleri kuyruğa alırız ve seviyeleri değiştirirken Boole bayrağının değerini tersine çeviririz.
Aşağıda yukarıdaki fikrin uygulanması yer almaktadır -
C++/* C++ program to print nodes of extreme corners of each level in alternate order */ #include
// Java program to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order import java.util.*; class GFG { // A binary tree node has data pointer to left child //and a pointer to right child / static class Node { int data; Node left right; }; // Helper function that allocates a new node with the //given data and null left and right pointers. / static Node newNode(int data) { Node node = new Node(); node.data = data; node.right = node.left = null; return node; } // Function to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order static void printExtremeNodes(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<Node>(); q.add(root); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed boolean flag = false; while (q.size()>0) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. int nodeCount = q.size(); int n = nodeCount; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (n-->0) { Node curr = q.peek(); // Enqueue left child if (curr.left!=null) q.add(curr.left); // Enqueue right child if (curr.right!=null) q.add(curr.right); // Dequeue node q.remove(); // if flag is true print leftmost node if (flag && n == nodeCount - 1) System.out.print( curr.data + ' '); // if flag is false print rightmost node if (!flag && n == 0) System.out.print( curr.data + ' '); } // invert flag for next level flag = !flag; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { // Binary Tree of Height 4 Node root = newNode(1); root.left = newNode(2); root.right = newNode(3); root.left.left = newNode(4); root.left.right = newNode(5); root.right.right = newNode(7); root.left.left.left = newNode(8); root.left.left.right = newNode(9); root.left.right.left = newNode(10); root.left.right.right = newNode(11); root.right.right.left = newNode(14); root.right.right.right = newNode(15); root.left.left.left.left = newNode(16); root.left.left.left.right = newNode(17); root.right.right.right.right = newNode(31); printExtremeNodes(root); } } // This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
# Python program to print nodes of extreme corners # of each level in alternate order # Utility class to create a node class Node: def __init__(self key): self.data = key self.left = self.right = None # Utility function to create a tree node def newNode( data): temp = Node(0) temp.data = data temp.left = temp.right = None return temp # Function to print nodes of extreme corners # of each level in alternate order def printExtremeNodes( root): if (root == None): return # Create a queue and enqueue left and right # children of root q = [] q.append(root) # flag to indicate whether leftmost node or # the rightmost node has to be printed flag = False while (len(q) > 0): # nodeCount indicates number of nodes # at current level. nodeCount = len(q) n = nodeCount # Dequeue all nodes of current level # and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (n > 0): n = n - 1 curr = q[0] # Enqueue left child if (curr.left != None): q.append(curr.left) # Enqueue right child if (curr.right != None): q.append(curr.right) # Dequeue node q.pop(0) # if flag is true print leftmost node if (flag and n == nodeCount - 1): print( curr.data end=' ') # if flag is false print rightmost node if (not flag and n == 0): print( curr.data end= ' ') # invert flag for next level flag = not flag # Driver program to test above functions # Binary Tree of Height 4 root = newNode(1) root.left = newNode(2) root.right = newNode(3) root.left.left = newNode(4) root.left.right = newNode(5) root.right.right = newNode(7) root.left.left.left = newNode(8) root.left.left.right = newNode(9) root.left.right.left = newNode(10) root.left.right.right = newNode(11) root.right.right.left = newNode(14) root.right.right.right = newNode(15) root.left.left.left.left = newNode(16) root.left.left.left.right = newNode(17) root.right.right.right.right = newNode(31) printExtremeNodes(root) # This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
// C# program to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { // A binary tree node has data pointer to left child //and a pointer to right child / public class Node { public int data; public Node left right; }; // Helper function that allocates a new node with the //given data and null left and right pointers. / static Node newNode(int data) { Node node = new Node(); node.data = data; node.right = node.left = null; return node; } // Function to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order static void printExtremeNodes(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); q.Enqueue(root); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed Boolean flag = false; while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. int nodeCount = q.Count; int n = nodeCount; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (n-->0) { Node curr = q.Peek(); // Enqueue left child if (curr.left != null) q.Enqueue(curr.left); // Enqueue right child if (curr.right != null) q.Enqueue(curr.right); // Dequeue node q.Dequeue(); // if flag is true print leftmost node if (flag && n == nodeCount - 1) Console.Write( curr.data + ' '); // if flag is false print rightmost node if (!flag && n == 0) Console.Write( curr.data + ' '); } // invert flag for next level flag = !flag; } } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { // Binary Tree of Height 4 Node root = newNode(1); root.left = newNode(2); root.right = newNode(3); root.left.left = newNode(4); root.left.right = newNode(5); root.right.right = newNode(7); root.left.left.left = newNode(8); root.left.left.right = newNode(9); root.left.right.left = newNode(10); root.left.right.right = newNode(11); root.right.right.left = newNode(14); root.right.right.right = newNode(15); root.left.left.left.left = newNode(16); root.left.left.left.right = newNode(17); root.right.right.right.right = newNode(31); printExtremeNodes(root); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
<script> // JavaScript program to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order // A binary tree node has data pointer to left child //and a pointer to right child / class Node { constructor() { this.data = 0; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }; // Helper function that allocates a new node with the //given data and null left and right pointers. / function newNode(data) { var node = new Node(); node.data = data; node.right = node.left = null; return node; } // Function to print nodes of extreme corners //of each level in alternate order function printExtremeNodes(root) { if (root == null) return; // Create a queue and enqueue left and right // children of root var q = []; q.push(root); // flag to indicate whether leftmost node or // the rightmost node has to be printed var flag = false; while (q.length > 0) { // nodeCount indicates number of nodes // at current level. var nodeCount = q.length; var n = nodeCount; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and push all nodes of next level while (n-->0) { var curr = q[0]; // push left child if (curr.left != null) q.push(curr.left); // push right child if (curr.right != null) q.push(curr.right); // Dequeue node q.shift(); // if flag is true print leftmost node if (flag && n == nodeCount - 1) document.write( curr.data + ' '); // if flag is false print rightmost node if (!flag && n == 0) document.write( curr.data + ' '); } // invert flag for next level flag = !flag; } } // Driver code // Binary Tree of Height 4 var root = newNode(1); root.left = newNode(2); root.right = newNode(3); root.left.left = newNode(4); root.left.right = newNode(5); root.right.right = newNode(7); root.left.left.left = newNode(8); root.left.left.right = newNode(9); root.left.right.left = newNode(10); root.left.right.right = newNode(11); root.right.right.left = newNode(14); root.right.right.right = newNode(15); root.left.left.left.left = newNode(16); root.left.left.left.right = newNode(17); root.right.right.right.right = newNode(31); printExtremeNodes(root); </script>
Çıkış
1 2 7 8 31
Zaman karmaşıklığı: O(n) burada n, belirli bir ikili ağaçtaki toplam düğüm sayısıdır.
Yardımcı Alan: O(n) burada n, belirli bir ikili ağaçta sıraya bağlı olarak düğümlerin toplam sayısıdır.
Egzersiz yapmak - Her düzeyin en uç köşelerindeki düğümleri aşağıdan yukarıya doğru alternatif sırayla yazdırın.
