Rastgele, NumPy kütüphanesinde bulunan bir modüldür. Bu modül rastgele sayılar üretmek için kullanılan fonksiyonları içerir. Bu modül bazı basit rastgele veri üretme yöntemlerini, bazı permütasyon ve dağıtım fonksiyonlarını ve rastgele üreteç fonksiyonlarını içerir.
Rastgele bir modüldeki tüm işlevler aşağıdaki gibidir:
Basit rastgele veriler
Basit rastgele verilerin aşağıdaki işlevleri vardır:
1) p.random.rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, belirli bir şekilde rastgele sayılar veya değerler üretmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.rand(5,2) a
Çıktı:
array([[0.74710182, 0.13306399], [0.01463718, 0.47618842], [0.98980426, 0.48390004], [0.58661785, 0.62895758], [0.38432729, 0.90384119]])
2) np.random.randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi 'standart normal' dağılımdan bir örnek döndürür.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.randn(2,2) a
Çıktı:
array([[ 1.43327469, -0.02019121], [ 1.54626422, 1.05831067]]) b=np.random.randn() b -0.3080190768904835
3) np.random.randint(düşük[, yüksek, boyut, dtype])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, dahil ediciden (düşük) dışlayıcıya (yüksek) kadar rastgele tamsayılar üretmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.randint(3, size=10) a
Çıktı:
array([1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
4) np.random.random_integers(düşük[, yüksek, boyut])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, düşük ve yüksek arasında np.int türünde rastgele tamsayılar üretmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.random_integers(3) a b=type(np.random.random_integers(3)) b c=np.random.random_integers(5, size=(3,2)) c
Çıktı:
2 array([[1, 1], [2, 5], [1, 3]])
5) np.random.random_sample([boyut])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, yarı açık aralıkta [0.0, 1.0] rastgele kayan nokta sayısı oluşturmak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.random_sample() a b=type(np.random.random_sample()) b c=np.random.random_sample((5,)) c
Çıktı:
0.09250360565571492 array([0.34665418, 0.47027209, 0.75944969, 0.37991244, 0.14159746])
6) np.random.random([boyut])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, yarı açık aralıkta [0.0, 1.0] rastgele kayan nokta sayısı oluşturmak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.random() a b=type(np.random.random()) b c=np.random.random((5,)) c
Çıktı:
0.008786953974334155 array([0.05530122, 0.59133394, 0.17258794, 0.6912388 , 0.33412534])
7) np.random.ranf([boyut])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, yarı açık aralıkta [0.0, 1.0] rastgele kayan nokta sayısı oluşturmak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.ranf() a b=type(np.random.ranf()) b c=np.random.ranf((5,)) c
Çıktı:
0.2907792098474542 array([0.34084881, 0.07268237, 0.38161256, 0.46494681, 0.88071377])
8) np.random.sample([boyut])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, yarı açık aralıkta [0.0, 1.0] rastgele kayan nokta sayısı oluşturmak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.sample() a b=type(np.random.sample()) b c=np.random.sample((5,)) c
Çıktı:
0.012298209913766511 array([0.71878544, 0.11486169, 0.38189074, 0.14303308, 0.07217287])
9) np.random.choice(a[, boyut, değiştir, p])
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi, belirli bir 1 boyutlu diziden rastgele örnek oluşturmak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.choice(5,3) a b=np.random.choice(5,3, p=[0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1]) b
Çıktı:
array([0, 3, 4]) array([2, 2, 2], dtype=int64)
10) np.random.bytes(uzunluk)
Rastgele modülün bu işlevi rastgele baytlar oluşturmak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
mylivecriclet
import numpy as np a=np.random.bytes(7) a
Çıktı:
'nQx08x83xf9xdex8a'
Permütasyonlar
Permütasyonların aşağıdaki işlevleri vardır:
1) np.random.shuffle()
Bu işlev, bir diziyi, içeriğini karıştırarak yerinde değiştirmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.arange(12) a np.random.shuffle(a) a
Çıktı:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) array([10, 3, 2, 4, 5, 8, 0, 9, 1, 11, 7, 6])
2) np.random.permutation()
Bu fonksiyon bir diziyi rastgele değiştirir veya permütasyonlu bir aralık döndürür.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a=np.random.permutation(12) a
Çıktı:
array([ 8, 7, 3, 11, 6, 0, 9, 10, 2, 5, 4, 1])
Dağılımlar
Permütasyonların aşağıdaki işlevleri vardır:
1) beta(a, b[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon bir Beta dağılımından örnekler çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
def setup(self): self.dist = dist.beta self.cargs = [] self.ckwd = dict(alpha=2, beta=3) self.np_rand_fxn = numpy.random.beta self.np_args = [2, 3] self.np_kwds = dict()
2) binom(n, p[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon binom dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np n, p = 10, .6 s1= np.random.binomial(n, p, 10) s1
Çıktı:
array([6, 7, 7, 9, 3, 7, 8, 6, 6, 4])
3) kikare(df[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon binom dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np np.random.chisquare(2,4) sum(np.random.binomial(9, 0.1, 20000) == 0)/20000.
Çıktı:
array([6, 7, 7, 9, 3, 7, 8, 6, 6, 4])
4) dirichlet(alfa[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon Dirichlet dağılımından bir örnek çizmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
Import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.dirichlet((10, 5, 3), 20).transpose() plt.barh(range(20), s1[0]) plt.barh(range(20), s1[1], left=s1[0], color='g') plt.barh(range(20), s1[2], left=s1[0]+s1[1], color='r') plt.title('Lengths of Strings') plt.show()
Çıktı:
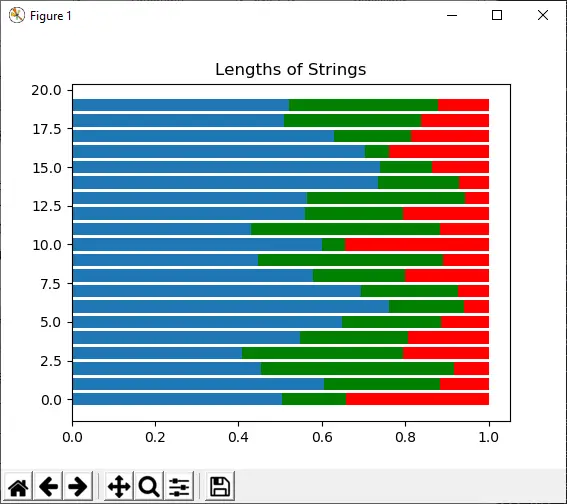
5) üstel([ölçek, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon üstel bir dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
def __init__(self, sourceid, targetid): self.__type = 'Transaction' self.id = uuid4() self.source = sourceid self.target = targetid self.date = self._datetime.date(start=2015, end=2019) self.time = self._datetime.time() if random() <0.05: self.amount="self._numbers.between(100000," 1000000) if random() < 0.15: self.currency="self._business.currency_iso_code()" else: pre> <p> <strong>6) f(dfnum, dfden[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from an F distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np dfno= 1. dfden = 48. s1 = np.random.f(dfno, dfden, 10) np.sort(s1) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([0.00264041, 0.04725478, 0.07140803, 0.19526217, 0.23979 , 0.24023478, 0.63141254, 0.95316446, 1.40281789, 1.68327507]) </pre> <p> <strong>7) gamma(shape[, scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Gamma distribution </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np shape, scale = 2., 2. s1 = np.random.gamma(shape, scale, 1000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.special as spss count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) a = bins**(shape-1)*(np.exp(-bins/scale) / (spss.gamma(shape)*scale**shape)) plt.plot(bins, a, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-2.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>8) geometric(p[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a geometric distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np a = np.random.geometric(p=0.35, size=10000) (a == 1).sum() / 1000 </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 3. </pre> <p> <strong>9) gumbel([loc, scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Gumble distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np lov, scale = 0, 0.2 s1 = np.random.gumbel(loc, scale, 1000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 30, density=True) plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*np.exp(-(bins - loc)/beta)* np.exp( -np.exp( -(bins - loc) /beta) ),linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-3.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>10) hypergeometric(ngood, nbad, nsample[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Hypergeometric distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np good, bad, samp = 100, 2, 10 s1 = np.random.hypergeometric(good, bad, samp, 1000) plt.hist(s1) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> (array([ 13., 0., 0., 0., 0., 163., 0., 0., 0., 824.]), array([ 8. , 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.8, 9. , 9.2, 9.4, 9.6, 9.8, 10. ]), <a 10 list of patch objects>) </a></pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-4.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>11) laplace([loc, scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from the Laplace or double exponential distribution with specified location and scale.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np location, scale = 0., 2. s = np.random.laplace(location, scale, 10) s </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([-2.77127948, -1.46401453, -0.03723516, -1.61223942, 2.29590691, 1.74297722, 1.49438411, 0.30325513, -0.15948891, -4.99669747]) </pre> <p> <strong>12) logistic([loc, scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from logistic distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt location, scale = 10, 1 s1 = np.random.logistic(location, scale, 10000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=50) count bins ignored plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 5.000e+00, 7.000e+00, 1.100e+01, 1.800e+01, 3.500e+01, 5.300e+01, 6.700e+01, 1.150e+02, 1.780e+02, 2.300e+02, 3.680e+02, 4.910e+02, 6.400e+02, 8.250e+02, 9.100e+02, 9.750e+02, 1.039e+03, 9.280e+02, 8.040e+02, 6.530e+02, 5.240e+02, 3.380e+02, 2.470e+02, 1.650e+02, 1.150e+02, 8.500e+01, 6.400e+01, 3.300e+01, 1.600e+01, 2.400e+01, 1.400e+01, 4.000e+00, 5.000e+00, 2.000e+00, 2.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00]) array([ 0.50643911, 0.91891814, 1.33139717, 1.7438762 , 2.15635523, 2.56883427, 2.9813133 , 3.39379233, 3.80627136, 4.2187504 , 4.63122943, 5.04370846, 5.45618749, 5.86866652, 6.28114556, 6.69362459, 7.10610362, 7.51858265, 7.93106169, 8.34354072, 8.75601975, 9.16849878, 9.58097781, 9.99345685, 10.40593588, 10.81841491, 11.23089394, 11.64337298, 12.05585201, 12.46833104, 12.88081007, 13.2932891 , 13.70576814, 14.11824717, 14.5307262 , 14.94320523, 15.35568427, 15.7681633 , 16.18064233, 16.59312136, 17.00560039, 17.41807943, 17.83055846, 18.24303749, 18.65551652, 19.06799556, 19.48047459, 19.89295362, 20.30543265, 20.71791168, 21.13039072]) <a 50 list of patch objects> </a></pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-5.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>13) lognormal([mean, sigma, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a log-normal distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np mu, sigma = 2., 1. s1 = np.random.lognormal(mu, sigma, 1000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 100, density=True, ) a = np.linspace(min(bins), max(bins), 10000) pdf = (np.exp(-(np.log(a) - mu)**2 / (2 * sigma**2))/ (a * sigma * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi))) plt.plot(a, pdf, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.axis('tight') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-6.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>14) logseries(p[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a logarithmic distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np x = .6 s1 = np.random.logseries(x, 10000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1) def logseries(k, p): return -p**k/(k*log(1-p)) plt.plot(bins, logseries(bins, x)*count.max()/logseries(bins, a).max(), 'r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-7.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>15) multinomial(n, pvals[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a multinomial distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np np.random.multinomial(20, [1/6.]*6, size=1) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([[4, 2, 5, 5, 3, 1]]) </pre> <p> <strong>16) multivariate_normal(mean, cov[, size, ...)</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a multivariate normal distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np mean = (1, 2) coveriance = [[1, 0], [0, 100]] import matplotlib.pyplot as plt a, b = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, coveriance, 5000).T plt.plot(a, b, 'x') plt.axis('equal'023 030 ) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-8.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>17) negative_binomial(n, p[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a negative binomial distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np s1 = np.random.negative_binomial(1, 0.1, 100000) for i in range(1, 11): probability = sum(s1 <i) 36 100000. print i, 'wells drilled, probability of one success=", probability </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 1 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 2 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 3 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 4 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 5 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 6 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 7 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 8 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 9 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 10 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 </pre> <p > <strong>18) noncentral_chisquare(df, nonc[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a noncentral chi-square distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt val = plt.hist(np.random.noncentral_chisquare(3, 25, 100000), bins=200, normed=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img numpy-tutorial numpy-random-python-9.webp' alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>19) normal([loc, scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a normal distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mu, sigma = 0, 0.2 # mean and standard deviation s1 = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 1000) abs(mu - np.mean(s1)) <0.01 1 abs(sigma - np.std(s1, ddof="1))" < 0.01 count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 30, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, (sigma * np.sqrt(2 np.pi)) *np.exp( (bins mu)**2 (2 sigma**2) ), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-10.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>20) pareto(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw samples from a Lomax or Pareto II with specified shape.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt b, m1 = 3., 2. # shape and mode s1 = (np.random.pareto(b, 1000) + 1) * m1 count, bins, _ = plt.hist(s1, 100, density=True) fit = b*m**b / bins**(b+1) plt.plot(bins, max(count)*fit/max(fit), linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-11.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>21) power(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw samples in [0, 1] from a power distribution with positive exponent a-1.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np x = 5. # shape samples = 1000 s1 = np.random.power(x, samples) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=30) a = np.linspace(0, 1, 100) b = x*a**(x-1.) density_b = samples*np.diff(bins)[0]*b plt.plot(a, density_b) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-12.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>22) rayleigh([scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Rayleigh distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> val = hist(np.random.rayleigh(3, 100000), bins=200, density=True) meanval = 1 modeval = np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * meanval s1 = np.random.rayleigh(modeval, 1000000) 100.*sum(s1>3)/1000000. </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 0.087300000000000003 </pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-13.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>23) standard_cauchy([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Cauchy distribution with mode=0.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.standard_cauchy(1000000) s1 = s1[(s1>-25) & (s1<25)] # truncate distribution so it plots well plt.hist(s1, bins="100)" plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-14.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>24) standard_exponential([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard exponential distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np n = np.random.standard_exponential((2, 7000)) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([[0.53857931, 0.181262 , 0.20478701, ..., 3.66232881, 1.83882709, 1.77963295], [0.65163973, 1.40001955, 0.7525986 , ..., 0.76516523, 0.8400617 , 0.88551011]]) </pre> <p> <strong>25) standard_gamma([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Gamma distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np shape, scale = 2., 1. s1 = np.random.standard_gamma(shape, 1000000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.special as sps count1, bins1, ignored1 = plt.hist(s, 50, density=True) y = bins1**(shape-1) * ((np.exp(-bins1/scale))/ (sps.gamma(shape) * scale**shape)) plt.plot(bins1, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-15.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>26) standard_normal([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Normal distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1= np.random.standard_normal(8000) s1 q = np.random.standard_normal(size=(3, 4, 2)) q </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([-3.14907597, 0.95366265, -1.20100026, ..., 3.47180222, 0.9608679 , 0.0774319 ]) array([[[ 1.55635461, -1.29541713], [-1.50534663, -0.02829194], [ 1.03949348, -0.26128132], [ 1.51921798, 0.82136178]], [[-0.4011052 , -0.52458858], [-1.31803814, 0.37415379], [-0.67077365, 0.97447018], [-0.20212115, 0.67840888]], [[ 1.86183474, 0.19946562], [-0.07376021, 0.84599701], [-0.84341386, 0.32081667], [-3.32016062, -1.19029818]]]) </pre> <p> <strong>27) standard_t(df[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Student's distribution with df degree of freedom.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> intake = np.array([5260., 5470, 5640, 6180, 6390, 6515, 6805, 7515,8230,8770]) s1 = np.random.standard_t(10, size=100000) np.mean(intake) intake.std(ddof=1) t = (np.mean(intake)-7725)/(intake.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(len(intake))) h = plt.hist(s1, bins=100, density=True) np.sum(s1<t) float(len(s1)) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 6677.5 1174.1101831694598 0.00864 </pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-16.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>28) triangular(left, mode, right[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a triangular distribution over the interval.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.triangular(-4, 0, 8, 1000000), bins=300,density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-17.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>29) uniform([low, high, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a uniform distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000) np.all(s1 >= -1) np.all(s1 <0) count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 15, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-18.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>30) vonmises(m1, m2[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a von Mises distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt m1, m2 = 0.0, 4.0 s1 = np.random.vonmises(m1, m2, 1000) from scipy.special import i0 plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, num=51) y = np.exp(m2*np.cos(x-m1))/(2*np.pi*i0(m2)) plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-19.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>31) wald(mean, scale[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Wald, or inverse Gaussian distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-20.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>32) weibull(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Weibull distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000) a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50. def weib(x, n, a): return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000)) a= np.arange(1,100.)/50. scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max() scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max() plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-21.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>33) zipf(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Zipf distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density="True)" a="np.arange(1.," 50.) b="a**(-x)" special.zetac(x) plt.plot(a, max(b), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-22.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <hr></50],></pre></0)></pre></t)></pre></25)]></pre></0.01></pre></i)></pre></0.05:>
Çıktı:
array([0.00264041, 0.04725478, 0.07140803, 0.19526217, 0.23979 , 0.24023478, 0.63141254, 0.95316446, 1.40281789, 1.68327507])
7) gamma(şekil[, ölçek, boyut])
Bu işlev bir Gama dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır
Örnek:
import numpy as np shape, scale = 2., 2. s1 = np.random.gamma(shape, scale, 1000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.special as spss count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) a = bins**(shape-1)*(np.exp(-bins/scale) / (spss.gamma(shape)*scale**shape)) plt.plot(bins, a, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show()

8) geometrik(p[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon geometrik bir dağılımdan örnek çizmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np a = np.random.geometric(p=0.35, size=10000) (a == 1).sum() / 1000
Çıktı:
3.
9) sakız([yer, ölçek, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon bir Gumble dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np lov, scale = 0, 0.2 s1 = np.random.gumbel(loc, scale, 1000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 30, density=True) plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*np.exp(-(bins - loc)/beta)* np.exp( -np.exp( -(bins - loc) /beta) ),linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show()
Çıktı:

10) hipergeometrik(niyi, nkötü, nörnek[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon Hipergeometrik dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np good, bad, samp = 100, 2, 10 s1 = np.random.hypergeometric(good, bad, samp, 1000) plt.hist(s1) plt.show()
Çıktı:
(array([ 13., 0., 0., 0., 0., 163., 0., 0., 0., 824.]), array([ 8. , 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.8, 9. , 9.2, 9.4, 9.6, 9.8, 10. ]), <a 10 list of patch objects>) </a>

11) laplace([yer, ölçek, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon, belirtilen konum ve ölçeğe sahip Laplace veya çift üstel dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np location, scale = 0., 2. s = np.random.laplace(location, scale, 10) s
Çıktı:
array([-2.77127948, -1.46401453, -0.03723516, -1.61223942, 2.29590691, 1.74297722, 1.49438411, 0.30325513, -0.15948891, -4.99669747])
12) lojistik([yer, ölçek, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon lojistik dağıtımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt location, scale = 10, 1 s1 = np.random.logistic(location, scale, 10000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=50) count bins ignored plt.show()
Çıktı:
array([1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 5.000e+00, 7.000e+00, 1.100e+01, 1.800e+01, 3.500e+01, 5.300e+01, 6.700e+01, 1.150e+02, 1.780e+02, 2.300e+02, 3.680e+02, 4.910e+02, 6.400e+02, 8.250e+02, 9.100e+02, 9.750e+02, 1.039e+03, 9.280e+02, 8.040e+02, 6.530e+02, 5.240e+02, 3.380e+02, 2.470e+02, 1.650e+02, 1.150e+02, 8.500e+01, 6.400e+01, 3.300e+01, 1.600e+01, 2.400e+01, 1.400e+01, 4.000e+00, 5.000e+00, 2.000e+00, 2.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00]) array([ 0.50643911, 0.91891814, 1.33139717, 1.7438762 , 2.15635523, 2.56883427, 2.9813133 , 3.39379233, 3.80627136, 4.2187504 , 4.63122943, 5.04370846, 5.45618749, 5.86866652, 6.28114556, 6.69362459, 7.10610362, 7.51858265, 7.93106169, 8.34354072, 8.75601975, 9.16849878, 9.58097781, 9.99345685, 10.40593588, 10.81841491, 11.23089394, 11.64337298, 12.05585201, 12.46833104, 12.88081007, 13.2932891 , 13.70576814, 14.11824717, 14.5307262 , 14.94320523, 15.35568427, 15.7681633 , 16.18064233, 16.59312136, 17.00560039, 17.41807943, 17.83055846, 18.24303749, 18.65551652, 19.06799556, 19.48047459, 19.89295362, 20.30543265, 20.71791168, 21.13039072]) <a 50 list of patch objects> </a>

13) lognormal([ortalama, sigma, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon log-normal dağılımdan örnek almak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np mu, sigma = 2., 1. s1 = np.random.lognormal(mu, sigma, 1000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 100, density=True, ) a = np.linspace(min(bins), max(bins), 10000) pdf = (np.exp(-(np.log(a) - mu)**2 / (2 * sigma**2))/ (a * sigma * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi))) plt.plot(a, pdf, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.axis('tight') plt.show()
Çıktı:

14) logserisi(p[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon logaritmik dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np x = .6 s1 = np.random.logseries(x, 10000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1) def logseries(k, p): return -p**k/(k*log(1-p)) plt.plot(bins, logseries(bins, x)*count.max()/logseries(bins, a).max(), 'r') plt.show()
Çıktı:

15) multinominal(n, pvals[, size])
Bu fonksiyon çok terimli bir dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np np.random.multinomial(20, [1/6.]*6, size=1)
Çıktı:
array([[4, 2, 5, 5, 3, 1]])
16) çok değişkenli_normal(ortalama, cov[, boyut, ...)
Bu fonksiyon çok değişkenli normal dağılımdan örnek almak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np mean = (1, 2) coveriance = [[1, 0], [0, 100]] import matplotlib.pyplot as plt a, b = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, coveriance, 5000).T plt.plot(a, b, 'x') plt.axis('equal'023 030 ) plt.show()
Çıktı:

17) negatif_binomial(n, p[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon negatif binom dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np s1 = np.random.negative_binomial(1, 0.1, 100000) for i in range(1, 11): probability = sum(s1 <i) 36 100000. print i, \'wells drilled, probability of one success=", probability </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 1 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 2 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 3 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 4 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 5 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 6 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 7 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 8 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 9 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 10 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 </pre> <p > <strong>18) noncentral_chisquare(df, nonc[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a noncentral chi-square distribution. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt val = plt.hist(np.random.noncentral_chisquare(3, 25, 100000), bins=200, normed=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img numpy-tutorial numpy-random-python-9.webp\' alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>19) normal([loc, scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a normal distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mu, sigma = 0, 0.2 # mean and standard deviation s1 = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 1000) abs(mu - np.mean(s1)) <0.01 1 abs(sigma - np.std(s1, ddof="1))" < 0.01 count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 30, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, (sigma * np.sqrt(2 np.pi)) *np.exp( (bins mu)**2 (2 sigma**2) ), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-10.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>20) pareto(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw samples from a Lomax or Pareto II with specified shape.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt b, m1 = 3., 2. # shape and mode s1 = (np.random.pareto(b, 1000) + 1) * m1 count, bins, _ = plt.hist(s1, 100, density=True) fit = b*m**b / bins**(b+1) plt.plot(bins, max(count)*fit/max(fit), linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-11.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>21) power(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw samples in [0, 1] from a power distribution with positive exponent a-1.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np x = 5. # shape samples = 1000 s1 = np.random.power(x, samples) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=30) a = np.linspace(0, 1, 100) b = x*a**(x-1.) density_b = samples*np.diff(bins)[0]*b plt.plot(a, density_b) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-12.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>22) rayleigh([scale, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Rayleigh distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> val = hist(np.random.rayleigh(3, 100000), bins=200, density=True) meanval = 1 modeval = np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * meanval s1 = np.random.rayleigh(modeval, 1000000) 100.*sum(s1>3)/1000000. </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 0.087300000000000003 </pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-13.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>23) standard_cauchy([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Cauchy distribution with mode=0.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.standard_cauchy(1000000) s1 = s1[(s1>-25) & (s1<25)] # truncate distribution so it plots well plt.hist(s1, bins="100)" plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-14.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>24) standard_exponential([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard exponential distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np n = np.random.standard_exponential((2, 7000)) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([[0.53857931, 0.181262 , 0.20478701, ..., 3.66232881, 1.83882709, 1.77963295], [0.65163973, 1.40001955, 0.7525986 , ..., 0.76516523, 0.8400617 , 0.88551011]]) </pre> <p> <strong>25) standard_gamma([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Gamma distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np shape, scale = 2., 1. s1 = np.random.standard_gamma(shape, 1000000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.special as sps count1, bins1, ignored1 = plt.hist(s, 50, density=True) y = bins1**(shape-1) * ((np.exp(-bins1/scale))/ (sps.gamma(shape) * scale**shape)) plt.plot(bins1, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-15.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>26) standard_normal([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Normal distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1= np.random.standard_normal(8000) s1 q = np.random.standard_normal(size=(3, 4, 2)) q </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([-3.14907597, 0.95366265, -1.20100026, ..., 3.47180222, 0.9608679 , 0.0774319 ]) array([[[ 1.55635461, -1.29541713], [-1.50534663, -0.02829194], [ 1.03949348, -0.26128132], [ 1.51921798, 0.82136178]], [[-0.4011052 , -0.52458858], [-1.31803814, 0.37415379], [-0.67077365, 0.97447018], [-0.20212115, 0.67840888]], [[ 1.86183474, 0.19946562], [-0.07376021, 0.84599701], [-0.84341386, 0.32081667], [-3.32016062, -1.19029818]]]) </pre> <p> <strong>27) standard_t(df[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Student's distribution with df degree of freedom.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> intake = np.array([5260., 5470, 5640, 6180, 6390, 6515, 6805, 7515,8230,8770]) s1 = np.random.standard_t(10, size=100000) np.mean(intake) intake.std(ddof=1) t = (np.mean(intake)-7725)/(intake.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(len(intake))) h = plt.hist(s1, bins=100, density=True) np.sum(s1<t) float(len(s1)) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 6677.5 1174.1101831694598 0.00864 </pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-16.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>28) triangular(left, mode, right[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a triangular distribution over the interval.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.triangular(-4, 0, 8, 1000000), bins=300,density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-17.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>29) uniform([low, high, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a uniform distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000) np.all(s1 >= -1) np.all(s1 <0) count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 15, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-18.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>30) vonmises(m1, m2[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a von Mises distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt m1, m2 = 0.0, 4.0 s1 = np.random.vonmises(m1, m2, 1000) from scipy.special import i0 plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, num=51) y = np.exp(m2*np.cos(x-m1))/(2*np.pi*i0(m2)) plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-19.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>31) wald(mean, scale[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Wald, or inverse Gaussian distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-20.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>32) weibull(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Weibull distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000) a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50. def weib(x, n, a): return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000)) a= np.arange(1,100.)/50. scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max() scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max() plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-21.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>33) zipf(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Zipf distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density="True)" a="np.arange(1.," 50.) b="a**(-x)" special.zetac(x) plt.plot(a, max(b), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-22.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <hr></50],></pre></0)></pre></t)></pre></25)]></pre></0.01></pre></i)>
Çıktı:

21) güç(a[, boyut])
sıralı geçiş
Bu fonksiyon, pozitif üssü a-1 olan bir güç dağılımından [0, 1]'deki örnekleri çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np x = 5. # shape samples = 1000 s1 = np.random.power(x, samples) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=30) a = np.linspace(0, 1, 100) b = x*a**(x-1.) density_b = samples*np.diff(bins)[0]*b plt.plot(a, density_b) plt.show()
Çıktı:

22) rayleigh([ölçek, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon Rayleigh dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
val = hist(np.random.rayleigh(3, 100000), bins=200, density=True) meanval = 1 modeval = np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * meanval s1 = np.random.rayleigh(modeval, 1000000) 100.*sum(s1>3)/1000000.
Çıktı:
0.087300000000000003

23) standart_cauchy([boyut])
Bu fonksiyon mod=0 olan standart bir Cauchy dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.standard_cauchy(1000000) s1 = s1[(s1>-25) & (s1<25)] # truncate distribution so it plots well plt.hist(s1, bins="100)" plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-14.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>24) standard_exponential([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard exponential distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np n = np.random.standard_exponential((2, 7000)) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([[0.53857931, 0.181262 , 0.20478701, ..., 3.66232881, 1.83882709, 1.77963295], [0.65163973, 1.40001955, 0.7525986 , ..., 0.76516523, 0.8400617 , 0.88551011]]) </pre> <p> <strong>25) standard_gamma([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Gamma distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np shape, scale = 2., 1. s1 = np.random.standard_gamma(shape, 1000000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.special as sps count1, bins1, ignored1 = plt.hist(s, 50, density=True) y = bins1**(shape-1) * ((np.exp(-bins1/scale))/ (sps.gamma(shape) * scale**shape)) plt.plot(bins1, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-15.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>26) standard_normal([size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Normal distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1= np.random.standard_normal(8000) s1 q = np.random.standard_normal(size=(3, 4, 2)) q </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> array([-3.14907597, 0.95366265, -1.20100026, ..., 3.47180222, 0.9608679 , 0.0774319 ]) array([[[ 1.55635461, -1.29541713], [-1.50534663, -0.02829194], [ 1.03949348, -0.26128132], [ 1.51921798, 0.82136178]], [[-0.4011052 , -0.52458858], [-1.31803814, 0.37415379], [-0.67077365, 0.97447018], [-0.20212115, 0.67840888]], [[ 1.86183474, 0.19946562], [-0.07376021, 0.84599701], [-0.84341386, 0.32081667], [-3.32016062, -1.19029818]]]) </pre> <p> <strong>27) standard_t(df[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a standard Student's distribution with df degree of freedom.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> intake = np.array([5260., 5470, 5640, 6180, 6390, 6515, 6805, 7515,8230,8770]) s1 = np.random.standard_t(10, size=100000) np.mean(intake) intake.std(ddof=1) t = (np.mean(intake)-7725)/(intake.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(len(intake))) h = plt.hist(s1, bins=100, density=True) np.sum(s1<t) float(len(s1)) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 6677.5 1174.1101831694598 0.00864 </pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-16.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>28) triangular(left, mode, right[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a triangular distribution over the interval.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.triangular(-4, 0, 8, 1000000), bins=300,density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-17.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>29) uniform([low, high, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a uniform distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000) np.all(s1 >= -1) np.all(s1 <0) count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 15, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-18.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>30) vonmises(m1, m2[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a von Mises distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt m1, m2 = 0.0, 4.0 s1 = np.random.vonmises(m1, m2, 1000) from scipy.special import i0 plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, num=51) y = np.exp(m2*np.cos(x-m1))/(2*np.pi*i0(m2)) plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-19.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>31) wald(mean, scale[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Wald, or inverse Gaussian distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-20.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>32) weibull(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Weibull distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000) a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50. def weib(x, n, a): return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000)) a= np.arange(1,100.)/50. scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max() scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max() plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-21.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>33) zipf(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Zipf distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density="True)" a="np.arange(1.," 50.) b="a**(-x)" special.zetac(x) plt.plot(a, max(b), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-22.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <hr></50],></pre></0)></pre></t)></pre></25)]>
Çıktı:
array([[0.53857931, 0.181262 , 0.20478701, ..., 3.66232881, 1.83882709, 1.77963295], [0.65163973, 1.40001955, 0.7525986 , ..., 0.76516523, 0.8400617 , 0.88551011]])
25) standart_gamma([boyut])
Bu işlev standart bir Gama dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np shape, scale = 2., 1. s1 = np.random.standard_gamma(shape, 1000000) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.special as sps count1, bins1, ignored1 = plt.hist(s, 50, density=True) y = bins1**(shape-1) * ((np.exp(-bins1/scale))/ (sps.gamma(shape) * scale**shape)) plt.plot(bins1, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show()
Çıktı:

26) standart_normal([boyut])
Bu işlev standart bir Normal dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1= np.random.standard_normal(8000) s1 q = np.random.standard_normal(size=(3, 4, 2)) q
Çıktı:
array([-3.14907597, 0.95366265, -1.20100026, ..., 3.47180222, 0.9608679 , 0.0774319 ]) array([[[ 1.55635461, -1.29541713], [-1.50534663, -0.02829194], [ 1.03949348, -0.26128132], [ 1.51921798, 0.82136178]], [[-0.4011052 , -0.52458858], [-1.31803814, 0.37415379], [-0.67077365, 0.97447018], [-0.20212115, 0.67840888]], [[ 1.86183474, 0.19946562], [-0.07376021, 0.84599701], [-0.84341386, 0.32081667], [-3.32016062, -1.19029818]]])
27) standart_t(df[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon, df serbestlik derecesine sahip standart bir Öğrenci dağılımından örnek almak için kullanılır.
Örnek:
intake = np.array([5260., 5470, 5640, 6180, 6390, 6515, 6805, 7515,8230,8770]) s1 = np.random.standard_t(10, size=100000) np.mean(intake) intake.std(ddof=1) t = (np.mean(intake)-7725)/(intake.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(len(intake))) h = plt.hist(s1, bins=100, density=True) np.sum(s1<t) float(len(s1)) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 6677.5 1174.1101831694598 0.00864 </pre> <p><img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-16.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"></p> <p> <strong>28) triangular(left, mode, right[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a triangular distribution over the interval.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.triangular(-4, 0, 8, 1000000), bins=300,density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-17.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>29) uniform([low, high, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a uniform distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000) np.all(s1 >= -1) np.all(s1 <0) count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 15, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-18.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>30) vonmises(m1, m2[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a von Mises distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt m1, m2 = 0.0, 4.0 s1 = np.random.vonmises(m1, m2, 1000) from scipy.special import i0 plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, num=51) y = np.exp(m2*np.cos(x-m1))/(2*np.pi*i0(m2)) plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-19.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>31) wald(mean, scale[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Wald, or inverse Gaussian distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-20.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>32) weibull(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Weibull distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000) a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50. def weib(x, n, a): return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000)) a= np.arange(1,100.)/50. scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max() scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max() plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-21.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>33) zipf(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Zipf distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density="True)" a="np.arange(1.," 50.) b="a**(-x)" special.zetac(x) plt.plot(a, max(b), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-22.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <hr></50],></pre></0)></pre></t)>

28) üçgen(sol, mod, sağ[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon aralık boyunca üçgen dağılımdan örnek çizmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.triangular(-4, 0, 8, 1000000), bins=300,density=True) plt.show()
Çıktı:

29) düzgün([düşük, yüksek, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon düzgün bir dağılımdan örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt s1 = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000) np.all(s1 >= -1) np.all(s1 <0) count, bins, ignored="plt.hist(s1," 15, density="True)" plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-18.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>30) vonmises(m1, m2[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a von Mises distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt m1, m2 = 0.0, 4.0 s1 = np.random.vonmises(m1, m2, 1000) from scipy.special import i0 plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True) x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, num=51) y = np.exp(m2*np.cos(x-m1))/(2*np.pi*i0(m2)) plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='r') plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-19.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>31) wald(mean, scale[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Wald, or inverse Gaussian distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-20.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>32) weibull(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Weibull distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000) a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50. def weib(x, n, a): return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000)) a= np.arange(1,100.)/50. scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max() scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max() plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale) plt.show() </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-21.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <p> <strong>33) zipf(a[, size])</strong> </p> <p>This function is used to draw sample from a Zipf distribution.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density="True)" a="np.arange(1.," 50.) b="a**(-x)" special.zetac(x) plt.plot(a, max(b), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-22.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <hr></50],></pre></0)>
Çıktı:

31) wald(ortalama, ölçek[, boyut])
Bu işlev bir Wald veya ters Gauss dağılımından örnek çizmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True) plt.show()
Çıktı:

32) weibull(a[, boyut])
Bu fonksiyon Weibull dağılımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000) a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50. def weib(x, n, a): return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000)) a= np.arange(1,100.)/50. scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max() scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max() plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale) plt.show()
Çıktı:

33) zipf(a[, boyut])
Bu işlev bir Zipf dağıtımından örnek çekmek için kullanılır.
Örnek:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import special x=2.0 s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000) count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density="True)" a="np.arange(1.," 50.) b="a**(-x)" special.zetac(x) plt.plot(a, max(b), linewidth="2," color="r" ) plt.show() < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/numpy-tutorial/36/numpy-random-python-22.webp" alt="numpy.random in Python"> <hr></50],>
