Bir dizi sabit boyuttadır, homojendir veri yapısı . Dizilerin sınırlaması boyutlarının sabit olmasıdır. Bu, diziyi bildirirken eleman sayısını belirtmemiz gerektiği anlamına gelir. Burada şu soru ortaya çıkıyor: Bir öğe eklemek istersek ve yeni öğe için daha fazla yer kalmazsa ne olur? Burada kavramın dinamik dizi meydana gelir. Dizinin boyutunu dinamik olarak genişletir.
Bu bölümde anlayacağız dinamik dizi nedir, dinamik dizinin özellikleri, dinamik dizi nasıl yeniden boyutlandırılır, Ve Java'da dinamik dizi nasıl uygulanacağı .
Dinamik dizi nedir?
Dinamik dizi bir değişken boyut veri yapısını listeleyin. Yeni eleman için yer kalmamışsa, eleman eklemeye çalıştığımızda otomatik olarak büyür. Öğe eklememizi ve çıkarmamızı sağlar. Yığın kullanarak çalışma zamanında bellek ayırır. Çalışma süresi boyunca boyutunu değiştirebilir.
İçinde Java , Dizi Listesi yeniden boyutlandırılabilir bir uygulamadır. Liste arayüzünü uygular ve liste işlemleriyle ilgili tüm yöntemleri sağlar. Dinamik dizinin gücü:
- Hızlı arama
- Değişken boyut
- Önbellek dostu
Dinamik Dizinin Çalışması
Dinamik dizide, öğeler dizinin başlangıcından itibaren bitişik olarak depolanır ve kalan alan kullanılmadan kalır. Ayrılmış boşluk tamamen tükenene kadar öğeleri ekleyebiliriz. Ayrılmış alan tüketildiğinde ve bazı öğelerin eklenmesi gerektiğinde. Böyle bir durumda sabit boyutlu dizinin boyutunun arttırılması gerekir. Öğeyi eklemeden önce daha büyük bir dizi ayırdığımızı, dizideki öğeleri kopyaladığımızı ve yeni oluşturulan diziyi döndürdüğümüzü unutmayın.
Bir öğe eklemenin başka bir yolu da, önce çift boyutlu yeni bir dizi oluşturan, eski dizideki tüm öğeleri kopyalayan ve yeni diziyi döndüren bir işlev oluşturmaktır. Benzer şekilde dinamik dizinin boyutunu da küçültebiliriz.
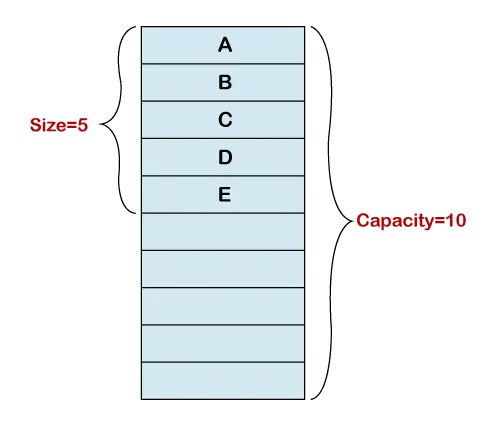
Boyut ve Kapasite
Dinamik bir dizinin başlatılması, sabit boyutlu bir dizi oluşturur. Aşağıdaki şekilde dizi uygulamasının 10 indeksi vardır. Diziye beş öğe ekledik. Artık temel dizinin uzunluğu beştir. Dolayısıyla dinamik dizi boyutunun uzunluğu 5, kapasitesi ise 10'dur. Dinamik dizi uç noktanın takibini yapar.
Dinamik Dizinin Özellikleri
Java'da dinamik dizinin üç temel özelliği vardır: Öğe ekleyin, bir öğeyi silin ve diziyi yeniden boyutlandırın.
dize java değiştir
Dinamik Diziye Öğe Ekleme
Dinamik dizide, diziye daha fazla öğe eklememiz gerekirse sabit boyutlu bir dizi oluşturabiliriz. Genellikle çift boyutlu yeni bir dizi oluşturur. Bundan sonra tüm elemanları yeni oluşturulan diziye kopyalar. Aşağıdaki yaklaşımı kullanıyoruz:

Dinamik Diziden Bir Öğeyi Silme
Belirtilen dizindeki diziden bir öğeyi kaldırmak istiyorsak, şunu kullanırız: kaldırAt(i) yöntem. Yöntem, silmek istediğimiz öğenin dizin numarasını ayrıştırır. Elemanı sildikten sonra kalan elemanları (silinen elemanın sağındaki elemanlar) belirtilen indeks numarasından sola kaydırır. Ayrıca dizinin sonundaki bir öğeyi silen Remove() yöntemini de kullanırız. Elemanları kaydırdıktan sonra saklar 0 son elementin sarayında. Aşağıdaki şekilde gösterdiğimiz gibi bir örnek üzerinden anlayalım.
yıldız desenini yazdır

Java'da Dinamik Diziyi Yeniden Boyutlandırma
Aşağıdaki durumlarda bir diziyi iki senaryoda yeniden boyutlandırmamız gerekir:
- Dizi gerekenden fazla bellek kullanıyor.
- Dizi tüm hafızayı kaplıyor ve eleman eklememiz gerekiyor.
İlk durumda, şunu kullanırız: küçültmeBoyutu() yeniden boyutlandırma yöntemi sıralamak . Dizinin boyutunu azaltır. Fazladan veya kullanılmayan belleği serbest bırakır. İkinci durumda, şunu kullanırız: büyümeBoyut() diziyi yeniden boyutlandırma yöntemi. Dizinin boyutunu artırır.
Bu pahalı bir işlemdir çünkü daha büyük bir dizi gerektirir ve önceki dizideki tüm öğeleri kopyaladıktan sonra yeni diziyi döndürür.

Yukarıdaki diziye altı öğe daha eklenmesi gerektiğini ve dizide öğeleri depolamak için daha fazla bellek kalmadığını varsayalım. Bu gibi durumlarda diziyi kullanarak büyütürüz. büyümeBoyut() yöntem.

Dinamik Dizi Başlatma
Dinamik dizinin başlatılması statik diziyle aynıdır. Dinamik bir diziyi başlatan aşağıdaki Java programını düşünün.
DynamicArray.java'yı başlat
public class InitializeDynamicArray { public static void main(String[] args) { //declaring array int array[]; //initialize an array array= new int[6]; //adding elements to the array array[0] = 34; array[1] = 90; array[2] = 12; array[3] = 22; array[4] = 9; array[5] = 27; System.out.print('Elements of Array are: '); //iteraton over the array for(int i=0; i <array.length ; i++) { system.out.print(array[i] +' '); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Elements of Array are: 34 90 12 22 9 27 </pre> <p>Let's implement the operations in a Java program that we have discussed above.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample1.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + ' '); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println('
elements after adding 5:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println('elements of array:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] ' '); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print('
elements element: system.out.print('no. da.count+'
'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;></pre></array.length> Yukarıda anlattığımız işlemleri bir Java programında gerçekleştirelim.
DynamicArrayExample1.java
public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + \' \'); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println(\'
elements after adding 5:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println(\'elements of array:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] \' \'); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print(\'
elements element: system.out.print(\'no. da.count+\'
\'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;>