2D dizi, dizilerden oluşan bir dizi olarak tanımlanabilir. 2B dizi, satır ve sütunların toplamı olarak temsil edilebilecek matrisler olarak düzenlenir.
Java'da soyutlama
Bununla birlikte, veri yapısına benzeyen ilişkisel bir veritabanı uygulamak için 2B diziler oluşturulur. Gerektiğinde herhangi bir sayıda fonksiyona aktarılabilen büyük miktarda veriyi aynı anda tutma kolaylığı sağlar.
2D Dizi nasıl bildirilir
İki boyutlu dizi bildirmenin sözdizimi, aşağıda verilen tek boyutlu diziye çok benzer.
int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
ancak aşağıdaki gibi görünen veri yapısını üretir.
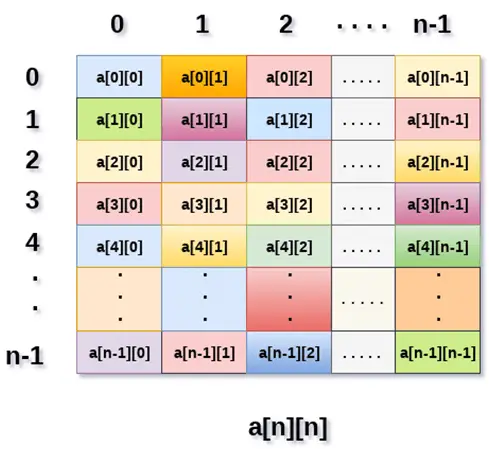
Yukarıdaki resim iki boyutlu diziyi göstermektedir; elemanlar satırlar ve sütunlar şeklinde düzenlenmiştir. İlk satırın ilk elemanı a[0][0] ile temsil edilir; burada birinci dizinde gösterilen sayı o satırın numarası, ikinci dizinde gösterilen sayı ise sütun numarasıdır.
2B dizideki verilere nasıl erişiriz?
Bunun nedeni 2 boyutlu dizilerin elemanlarına rastgele erişilebilmesidir. Tek boyutlu dizilere benzer şekilde, 2 boyutlu bir dizideki tek tek hücrelere hücrelerin indekslerini kullanarak erişebiliriz. Belirli bir hücreye bağlı iki indeks vardır; biri satır numarası, diğeri sütun numarasıdır.
Bununla birlikte, 2 boyutlu bir dizinin herhangi bir hücresinde saklanan değeri, aşağıdaki sözdizimini kullanarak bazı x değişkenlerine kaydedebiliriz.
int x = a[i][j];
burada i ve j sırasıyla hücrenin satır ve sütun numarasıdır.
Aşağıdaki kodu kullanarak 2 boyutlu bir dizinin her hücresini 0'a atayabiliriz:
for ( int i=0; i<n ;i++) { for (int j="0;" j<n; j++) a[i][j]="0;" } < pre> <h2>Initializing 2D Arrays </h2> <p>We know that, when we declare and initialize one dimensional array in C programming simultaneously, we don't need to specify the size of the array. However this will not work with 2D arrays. We will have to define at least the second dimension of the array. </p> <p>The syntax to declare and initialize the 2D array is given as follows. </p> <pre> int arr[2][2] = {0,1,2,3}; </pre> <p>The number of elements that can be present in a 2D array will always be equal to ( <strong>number of rows * number of columns</strong> ). </p> <p> <strong>Example :</strong> Storing User's data into a 2D array and printing it. </p> <p> <strong>C Example : </strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf('enter a[%d][%d]: ',i,j); scanf('%d',&arr[i][j]); } printf('
printing the elements ....
'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf('
'); printf('%d ',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print('enter element'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println('printing elements...'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+' '); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline('enter element'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline('printing elements...'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+' '); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></n> 2B dizide bulunabilecek öğelerin sayısı her zaman ( satır sayısı * sütun sayısı ).
Örnek : Kullanıcının verilerinin 2 boyutlu bir dizide saklanması ve yazdırılması.
Örnek :
#include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf(\'enter a[%d][%d]: \',i,j); scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i][j]); } printf(\'
printing the elements ....
\'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf(\'
\'); printf(\'%d \',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print(\'enter element\'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println(\'printing elements...\'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+\' \'); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline(\'enter element\'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline(\'printing elements...\'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+\' \'); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)> burada B. A., a[0][0] dizisinin temel adresi veya ilk öğesinin adresidir.
Örnek :
a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer
Sütun ana sırasına göre
Dizi, m'nin satır sayısı, n'nin ise sütun sayısı olduğu a[m][n] ile bildirilirse, o zaman ana satır sırasına göre saklanan dizinin a[i][j] öğesinin adresi şu şekilde hesaplanır: ,
Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA
burada BA dizinin temel adresidir.
Örnek:
A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes
