While döngüsü, önceden test edilmiş bir döngü olarak da bilinir. Genel olarak while döngüsü, kodun bir kısmının belirli bir boole koşuluna bağlı olarak birden çok kez yürütülmesine olanak tanır. Tekrarlanan bir if ifadesi olarak görülebilir. While döngüsü çoğunlukla yineleme sayısının önceden bilinmediği durumlarda kullanılır.
C dilinde while döngüsünün sözdizimi
C dilinde while döngüsünün sözdizimi aşağıda verilmiştir:
while(condition){ //code to be executed } C'deki while döngüsünün akış şeması
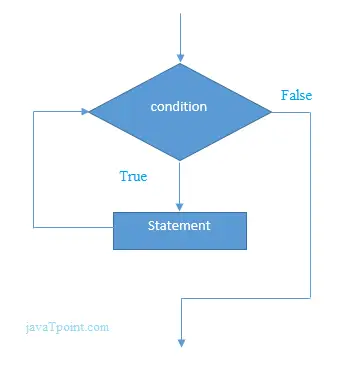
C dilinde while döngüsü örneği
Şimdi 1 tablosunu yazdıran while döngüsünün basit programını görelim.
#include int main(){ int i=1; while(i<=10){ printf('%d
',i); i++; } return 0; < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 </pre> <h2>Program to print table for the given number using while loop in C</h2> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=1,number=0,b=9; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); while(i<=10){ printf('%d
',(number*i)); i++; } return 0; < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> Enter a number: 50 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 </pre> <hr> <h2>Properties of while loop</h2> <ul> <li>A conditional expression is used to check the condition. The statements defined inside the while loop will repeatedly execute until the given condition fails.</li> <li>The condition will be true if it returns 0. The condition will be false if it returns any non-zero number.</li> <li>In while loop, the condition expression is compulsory.</li> <li>Running a while loop without a body is possible.</li> <li>We can have more than one conditional expression in while loop.</li> <li>If the loop body contains only one statement, then the braces are optional.</li> </ul> <h4>Example 1</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int j = 1; while(j+=2,j<=10) { printf('%d ',j); } printf('%d',j); < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 3 5 7 9 11 </pre> <h4>Example 2</h4> <pre> #include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> compile time error: while loop can't be empty </pre> <h4>Example 3</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h2>Infinitive while loop in C</h2> <p>If the expression passed in while loop results in any non-zero value then the loop will run the infinite number of times.</p> <pre> while(1){ //statement } </pre></=10)></pre></=10){></pre></=10){> C'de while döngüsünü kullanarak verilen sayıya ilişkin tabloyu yazdıran program
#include int main(){ int i=1,number=0,b=9; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); while(i<=10){ printf(\'%d
\',(number*i)); i++; } return 0; < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> Enter a number: 50 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 </pre> <hr> <h2>Properties of while loop</h2> <ul> <li>A conditional expression is used to check the condition. The statements defined inside the while loop will repeatedly execute until the given condition fails.</li> <li>The condition will be true if it returns 0. The condition will be false if it returns any non-zero number.</li> <li>In while loop, the condition expression is compulsory.</li> <li>Running a while loop without a body is possible.</li> <li>We can have more than one conditional expression in while loop.</li> <li>If the loop body contains only one statement, then the braces are optional.</li> </ul> <h4>Example 1</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int j = 1; while(j+=2,j<=10) { printf(\'%d \',j); } printf(\'%d\',j); < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 3 5 7 9 11 </pre> <h4>Example 2</h4> <pre> #include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> compile time error: while loop can't be empty </pre> <h4>Example 3</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h2>Infinitive while loop in C</h2> <p>If the expression passed in while loop results in any non-zero value then the loop will run the infinite number of times.</p> <pre> while(1){ //statement } </pre></=10)></pre></=10){> Enter a number: 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
While döngüsünün özellikleri
- Koşulu kontrol etmek için koşullu ifade kullanılır. While döngüsünde tanımlanan ifadeler, verilen koşul başarısız olana kadar tekrar tekrar yürütülür.
- Koşul 0 değerini döndürürse doğru olur. Sıfırdan farklı bir sayı döndürürse koşul yanlış olur.
- While döngüsünde koşul ifadesi zorunludur.
- Bir while döngüsünü body olmadan çalıştırmak mümkündür.
- While döngüsünde birden fazla koşullu ifademiz olabilir.
- Döngü gövdesi yalnızca bir ifade içeriyorsa parantezler isteğe bağlıdır.
örnek 1
#include void main () { int j = 1; while(j+=2,j<=10) { printf(\'%d \',j); } printf(\'%d\',j); < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 3 5 7 9 11 </pre> <h4>Example 2</h4> <pre> #include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> compile time error: while loop can't be empty </pre> <h4>Example 3</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h2>Infinitive while loop in C</h2> <p>If the expression passed in while loop results in any non-zero value then the loop will run the infinite number of times.</p> <pre> while(1){ //statement } </pre></=10)> Örnek 2
#include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } Çıktı
compile time error: while loop can't be empty
Örnek 3
#include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } Çıktı
infinite loop
C'de sonsuz while döngüsü
Eğer while döngüsüne aktarılan ifade sıfırdan farklı bir değerle sonuçlanırsa döngü sonsuz sayıda çalışacaktır.
while(1){ //statement } 