Boyutları dikdörtgen bir kağıt verildiğinde axb . Görev, kağıdın tamamını kesmektir. minimum sayısı kare parçalar. İstediğiniz büyüklükte kare parçalar seçebiliriz ancak bunların kesilmesi gerekir üst üste binmeden veya fazladan boşluk bırakmadan .
Örnekler:
Giriş: bir = 5 b = 8
Rudyard Kipling tarafından yapılan açıklama5 X 8 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 5 kare
Çıkış: 5
Açıklama: Kağıdı 5 kareye kesebiliriz: 5x5 boyutunda 1 kare, 3x3 boyutunda 1 kare, 2x2 boyutunda 1 kare ve 1x1 boyutunda 2 kare.Giriş: bir = 13 b = 11
13 X 11 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 6 kare
Çıkış: 6
Açıklama: Kağıdı 6 kareye kesebiliriz: 1 adet 7x7 boyutunda kare, 1 adet 6x6 boyutunda kare, 1 adet 5x5 boyutunda kare, 2 adet 4x4 boyutunda kare ve 1 adet 1x1 boyutunda kare.Giriş: bir = 6 b = 7
6 X 7 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 5 kare
Çıkış: 5
Açıklama: Kağıdı 5 kareye kesebiliriz: 4x4 boyutunda 1 kare, 3x3 boyutunda 2 kare ve 3x3 boyutunda 2 kare.np demek
İçerik Tablosu
- [Yanlış Yaklaşım 1] Açgözlü Tekniği Kullanmak
- [Yanlış Yaklaşım 2] Dinamik Programlamayı Kullanmak
- [Doğru Yaklaşım] DFS ve Dinamik Programlamayı Kullanma
[Yanlış Yaklaşım 1] Açgözlü Tekniği Kullanmak
İlk bakışta, ilk önce kağıttan mümkün olan en büyük kareyi keserek, ardından kalan kağıttan en büyük kareyi keserek ve tüm kağıdı kesene kadar bu şekilde devam ederek sorun kolayca çözülebilir gibi görünebilir. Fakat bu çözüm yanlıştır.
Açgözlü Yaklaşım neden işe yaramıyor?
boyutunda bir kağıt düşünün 6x7 o zaman eğer açgözlülükle kağıdı kesmeye çalışırsak, 7 kareler: 1 büyüklükteki kare 6x6 ve 6 kare boyutunda 1x1 oysa doğru çözüm şudur: 5. Dolayısıyla açgözlü yaklaşım işe yaramayacaktır.
[Yanlış Yaklaşım 2] Dinamik Programlamayı Kullanmak
Dinamik Programlama dikey veya yatay kesimlerle: Doğru görünebilecek başka bir çözüm de kullanmaktır. Dinamik Programlama . Öyle bir dp[][] tablosunu koruyabiliriz ki dp[i][j] = boyutlu kağıttan kesilebilecek minimum kare sayısı ben xj . Daha sonra kağıt boyutu için balta
- Her satır boyunca kesmeyi deneyebiliriz: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) burada k [1 i - 1] aralığında olabilir.
- Her sütun boyunca kesmeyi deneyebiliriz: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) burada k [1 j - 1] aralığında olabilir.
Son olarak tüm kesintilerin minimumu cevap olacaktır. Ancak bu çözüm de yanlıştır.
Dinamik Programlama Yaklaşımı ile dikey veya yatay kesim yapmak neden işe yaramıyor?
Bu işe yaramayacaktır çünkü dikey veya yatay kesmenin dikdörtgeni her zaman iki parçaya böleceğini varsayıyoruz. boyutunda bir kağıt düşünün 13x11 o zaman kağıdı DP yaklaşımını kullanarak kesmeye çalışırsak 8 kare elde ederiz ancak doğru cevap (Örneklerde gösterildiği gibi) 6'dır. Bu nedenle Dinamik Programlama çalışmaz.
[Doğru Yaklaşım] DFS ve Dinamik Programlamayı Kullanma
C++fikir kullanarak tüm kağıdı kesmektir. DFS içinde altüst biçim. Her adımda kağıdın sol alt köşesini bulun ve bu köşeden mümkün olan her boyutta kareler kesmeye çalışın. Bir kareyi kestikten sonra, mümkün olan tüm boyutlarda kareler kesmek için kalan kağıdın sol alt köşesini tekrar bulun. Ancak mümkün olan her kağıt boyutunun sol alt köşesinden mümkün olan tüm kesimleri denersek, bu oldukça verimsiz olacaktır. Bunu kullanarak optimize edebiliriz. Dinamik Programlama mümkün olan her kağıt boyutu için minimum kesimleri depolamak için.
Herhangi bir kağıt boyutunu benzersiz bir şekilde tanımlamak için, remSq[i]'nin kağıdın i'inci sütununda kalan 1x1 boyutunda kalan karelerin sayısını depolayacağı şekilde bir remSq[] dizisini koruyabiliriz. Yani 6x7 boyutunda bir kağıt için remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Ayrıca sol alt köşeyi bulmak için kalan maksimum karelere sahip ilk dizini bulacağız. Böylece remSq[] dizisinin tüm olası değerleri için benzersiz bir anahtar bulmak amacıyla remSq[] dizisinin değerini hash edebiliriz.
milyarda kaç 0
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Çıkış
6
Zaman Karmaşıklığı: O(a^b) b sütunlarının her biri için bir kareye sahip olabiliriz.
Yardımcı Alan: O(a^b) her benzersiz durumu saklayan not alma nedeniyle.

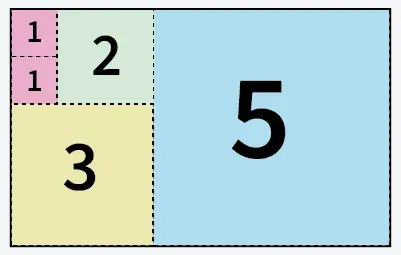 5 X 8 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 5 kare
5 X 8 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 5 kare 13 X 11 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 6 kare
13 X 11 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 6 kare 6 X 7 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 5 kare
6 X 7 ebadındaki kağıttan kesilmiş 5 kare