Python büyük/küçük harfe duyarlı bir programlama dilidir; bu, dilin büyük ve küçük harfleri farklı şekilde ele aldığı anlamına gelir. Örneğin Python'da 'x' değişkeni 'X' değişkeniyle aynı değildir. Bu davranış, JavaScript gibi büyük/küçük harfe duyarlı olmayan diğer bazı programlama dillerinden farklıdır.
Python'da değişken adları, işlev adları ve anahtar sözcüklerin tümü büyük/küçük harfe duyarlıdır. Bu, eğer bir 'x' değişkeni tanımlarsanız ve daha sonra ona 'X' olarak atıfta bulunmayı denerseniz, Python'un onu farklı bir değişken olarak ele alacağı ve bir hata alacağınız anlamına gelir. Benzer şekilde, 'Print' yerine 'print' fonksiyonunu çağırmaya çalışırsanız Python da size hata verecektir.
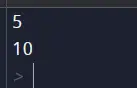
Python'da büyük/küçük harf duyarlılığının değişken adlarını nasıl etkilediğine dair bir örnek:
x = 5 X = 10 print(x) # Output: 5 print(X) # Output: 10
Çıktı
Java'daki koleksiyonlar
Açıklama:
Bu örnekte 'x' ve 'X' olmak üzere iki değişkeni farklı değerlerle tanımladık. Bunları yazdırdığımızda Python'un bunları ayrı değişkenler olarak ele aldığını ve onlara farklı değerler atadığını görüyoruz.
Büyük/küçük harf duyarlılığı Python'daki işlev adları için de geçerlidir. Örneğin:
print('Hello, World!') # Output: Hello, World! Print('Hello, World!') # Output: NameError: name 'Print' is not defined
Çıktı

Açıklama:
yerleşik 'print()' işlevi 'Print()' işlevinden farklıdır. İlki beklendiği gibi çalışacak, ikincisi ise tanımlanmış bir fonksiyon olmadığı için hata verecektir.
Python'daki anahtar kelimeler de büyük/küçük harfe duyarlıdır. Bu, 'if' veya 'for' gibi bir anahtar kelimeyi küçük harfle kullanırsanız beklendiği gibi çalışacağı anlamına gelir. Ancak, eğer onu büyük harfle kullanırsanız, Python bunu bir değişken adı olarak değerlendirecek ve bir hata alacaksınız.
Kaynak kodu:
if x <10: print('x is less than 10') if x < 10: # output: nameerror: name 'if' not defined pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/48/is-python-case-sensitive-3.webp" alt="Is Python Case Sensitive"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we have created two if statements. In the first if statement, we have used the proper syntax as Python is case-sensitive. We have created the first if statement with small i, and the second if statement has a capital I which means it is not correct syntax, so it will throw an error.</p> <p>In addition to variable names, function names, and keywords, Python is also case-sensitive when it comes to file names. This means that the file 'example.txt' is different from the file 'Example.txt,' and the interpreter will treat them as separate files.</p> <p>It is important to keep in mind that Python is case-sensitive when naming variables, functions, and keywords. This can lead to errors and unexpected behavior if you're not careful. To avoid these issues, it is a good practice to use a consistent naming convention, such as using lowercase letters for all variable and function names.</p> <p>In conclusion, Python is a case-sensitive programming language. This means that the language treats uppercase and lowercase characters differently. This applies to variable names, function names, keywords, and file names. It's important to keep in mind that case sensitivity can lead to errors and unexpected behavior if you're not careful, so it's a good practice to use a consistent naming convention.</p> <hr></10:>