Java GridLayout sınıfı, bileşenleri dikdörtgen bir ızgarada düzenlemek için kullanılır. Her dikdörtgende bir bileşen görüntülenir.
GridLayout sınıfının yapıcıları
GridLayout sınıfı örneği: GridLayout() Yapıcısını Kullanma
GridLayout() yapıcısı yalnızca bir satır oluşturur. Aşağıdaki örnek parametresiz yapıcının kullanımını göstermektedir.
javascript base64 kod çözme
Dosya adı: GridLayoutExample.java
// import statements import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class GridLayoutExample { JFrame frameObj; // constructor GridLayoutExample() { frameObj = new JFrame(); // creating 9 buttons JButton btn1 = new JButton('1'); JButton btn2 = new JButton('2'); JButton btn3 = new JButton('3'); JButton btn4 = new JButton('4'); JButton btn5 = new JButton('5'); JButton btn6 = new JButton('6'); JButton btn7 = new JButton('7'); JButton btn8 = new JButton('8'); JButton btn9 = new JButton('9'); // adding buttons to the frame // since, we are using the parameterless constructor, therfore; // the number of columns is equal to the number of buttons we // are adding to the frame. The row count remains one. frameObj.add(btn1); frameObj.add(btn2); frameObj.add(btn3); frameObj.add(btn4); frameObj.add(btn5); frameObj.add(btn6); frameObj.add(btn7); frameObj.add(btn8); frameObj.add(btn9); // setting the grid layout using the parameterless constructor frameObj.setLayout(new GridLayout()); frameObj.setSize(300, 300); frameObj.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new GridLayoutExample(); } } Çıktı:
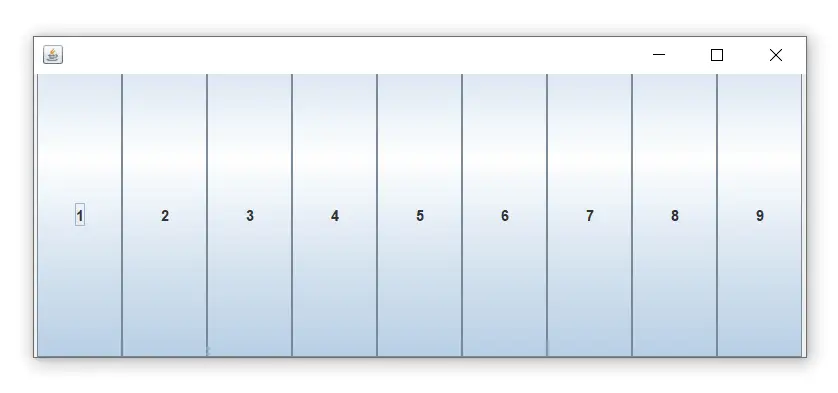
GridLayout sınıfı örneği: GridLayout(int satırlar, int sütunlar) Yapıcısını kullanma
Dosya adı: MyGridLayout.java
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class MyGridLayout{ JFrame f; MyGridLayout(){ f=new JFrame(); JButton b1=new JButton('1'); JButton b2=new JButton('2'); JButton b3=new JButton('3'); JButton b4=new JButton('4'); JButton b5=new JButton('5'); JButton b6=new JButton('6'); JButton b7=new JButton('7'); JButton b8=new JButton('8'); JButton b9=new JButton('9'); // adding buttons to the frame f.add(b1); f.add(b2); f.add(b3); f.add(b4); f.add(b5); f.add(b6); f.add(b7); f.add(b8); f.add(b9); // setting grid layout of 3 rows and 3 columns f.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,3)); f.setSize(300,300); f.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { new MyGridLayout(); } } Çıktı:
 bu örneği indir
bu örneği indirGridLayout sınıfı örneği: GridLayout(int satırlar, int sütunlar, int hgap, int vgap) Yapıcısını kullanma
Aşağıdaki örnek, parametreli GridLayout(int satırlar, int sütunlar, int hgap, int vgap) yapıcısını kullanarak düğmeler arasına yatay ve dikey boşluklar ekler.
Dosya adı: GridLayoutÖrnek1.java
js'de base64 kod çözme
// import statements import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class GridLayoutExample1 { JFrame frameObj; // constructor GridLayoutExample1() { frameObj = new JFrame(); // creating 9 buttons JButton btn1 = new JButton('1'); JButton btn2 = new JButton('2'); JButton btn3 = new JButton('3'); JButton btn4 = new JButton('4'); JButton btn5 = new JButton('5'); JButton btn6 = new JButton('6'); JButton btn7 = new JButton('7'); JButton btn8 = new JButton('8'); JButton btn9 = new JButton('9'); // adding buttons to the frame // since, we are using the parameterless constructor, therefore; // the number of columns is equal to the number of buttons we // are adding to the frame. The row count remains one. frameObj.add(btn1); frameObj.add(btn2); frameObj.add(btn3); frameObj.add(btn4); frameObj.add(btn5); frameObj.add(btn6); frameObj.add(btn7); frameObj.add(btn8); frameObj.add(btn9); // setting the grid layout // a 3 * 3 grid is created with the horizontal gap 20 // and vertical gap 25 frameObj.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 3, 20, 25)); frameObj.setSize(300, 300); frameObj.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new GridLayoutExample(); } } Çıktı:

