C++'da kalıtım, bir nesnenin ana nesnesinin tüm özelliklerini ve davranışlarını otomatik olarak edindiği bir süreçtir. Bu sayede diğer sınıfta tanımlanan özellik ve davranışları yeniden kullanabilir, genişletebilir veya değiştirebilirsiniz.
C++'da başka bir sınıfın üyelerini miras alan sınıfa türetilmiş sınıf, üyeleri miras alınan sınıfa ise temel sınıf adı verilir. Türetilmiş sınıf, temel sınıf için uzmanlaşmış sınıftır.
C++ Mirasının Avantajı
Kodun yeniden kullanılabilirliği: Artık ana sınıfınızın üyelerini yeniden kullanabilirsiniz. Yani üyeyi tekrar tanımlamaya gerek yok. Yani sınıfta daha az kod gerekir.
html'den js işlevini çağırmak
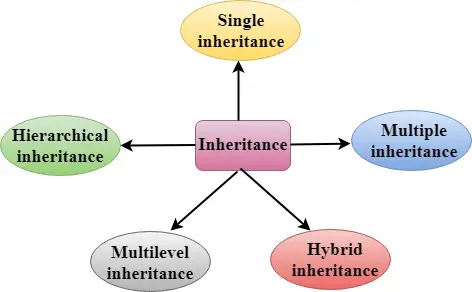
Miras Türleri
C++ beş tür kalıtımı destekler:
- Tek miras
- Çoklu kalıtım
- Hiyerarşik miras
- Çok düzeyli miras
- Hibrit kalıtım
Türetilmiş Sınıflar
Türetilmiş sınıf, temel sınıftan türetilen sınıf olarak tanımlanır.
str'den int'ye
Türetilmiş sınıfın Sözdizimi:
|_+_|Yukarıdaki durumda, türetilmiş sınıfın işlevi, temel sınıfın yöntemini geçersiz kılar. Bu nedenle, display() işlevine yapılan çağrı, türetilmiş sınıfta tanımlanan işlevi çağıracaktır. Temel sınıf fonksiyonunu çağırmak istersek sınıf çözümleme operatörünü kullanabiliriz.
int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } C++ Hibrit Kalıtım
Hibrit kalıtım birden fazla kalıtım türünün birleşimidir.

Basit bir örnek görelim:
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int a; public: void get_a() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'a' : ' <>a; } }; class B : public A { protected: int b; public: void get_b() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'b' : ' <>b; } }; class C { protected: int c; public: void get_c() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of c is : ' <>c; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int d; public: void mul() { get_a(); get_b(); get_c(); std::cout << 'Multiplication of a,b,c is : ' < <a*b*c<< std::endl; } }; int main() { d d; d.mul(); return 0; < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the value of 'a' : 10 Enter the value of 'b' : 20 Enter the value of c is : 30 Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000 </pre> <h2>C++ Hierarchical Inheritance</h2> <p>Hierarchical inheritance is defined as the process of deriving more than one class from a base class.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/62/c-inheritance-7.webp" alt="C++ Inheritance"> <p> <strong>Syntax of Hierarchical inheritance:</strong> </p> <pre> class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } </pre> <p>Let's see a simple example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<></pre></a*b*c<<> C++ Hiyerarşik Kalıtım
Hiyerarşik miras, bir temel sınıftan birden fazla sınıfın türetilmesi süreci olarak tanımlanır.

Hiyerarşik mirasın sözdizimi:
class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } Basit bir örnek görelim:
Java liste düğümü
#include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<>